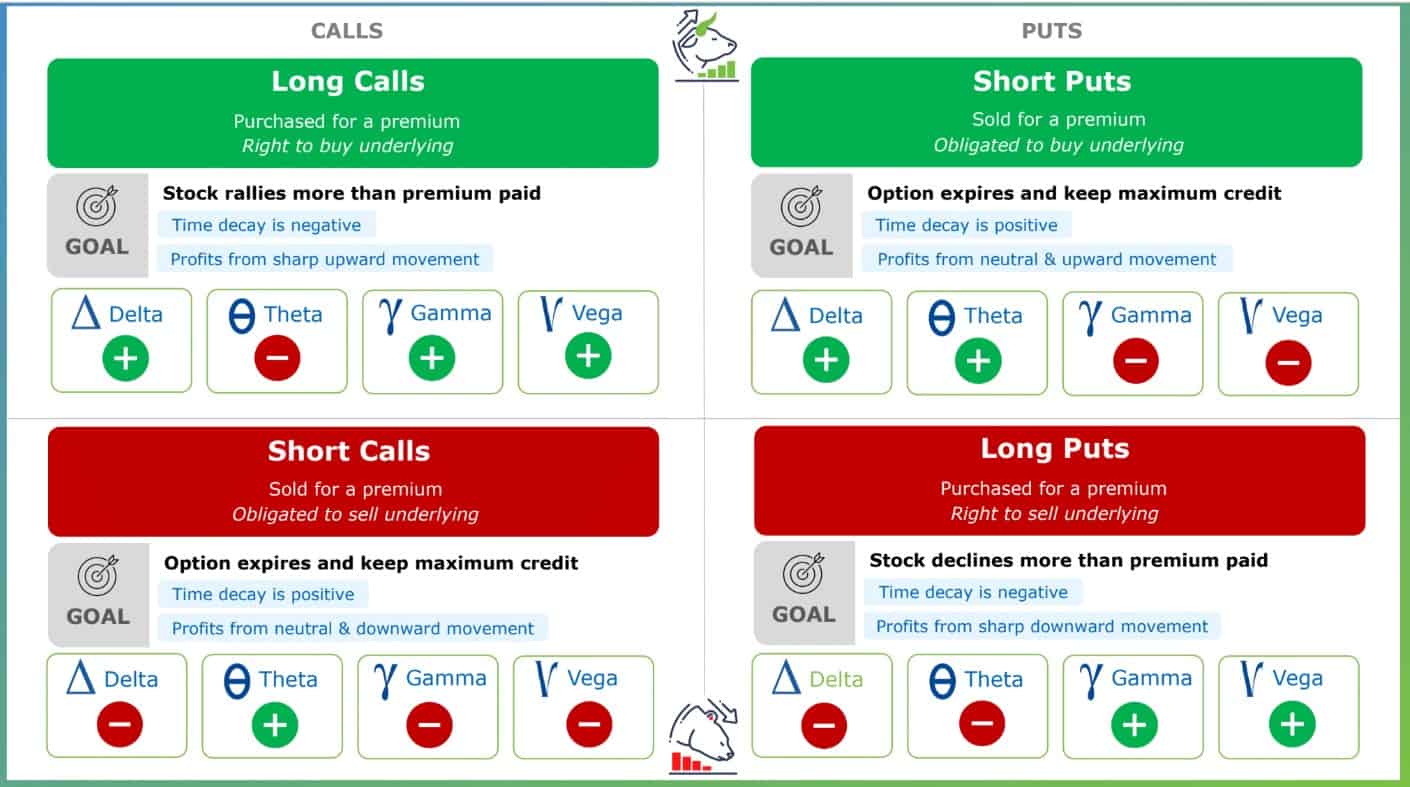
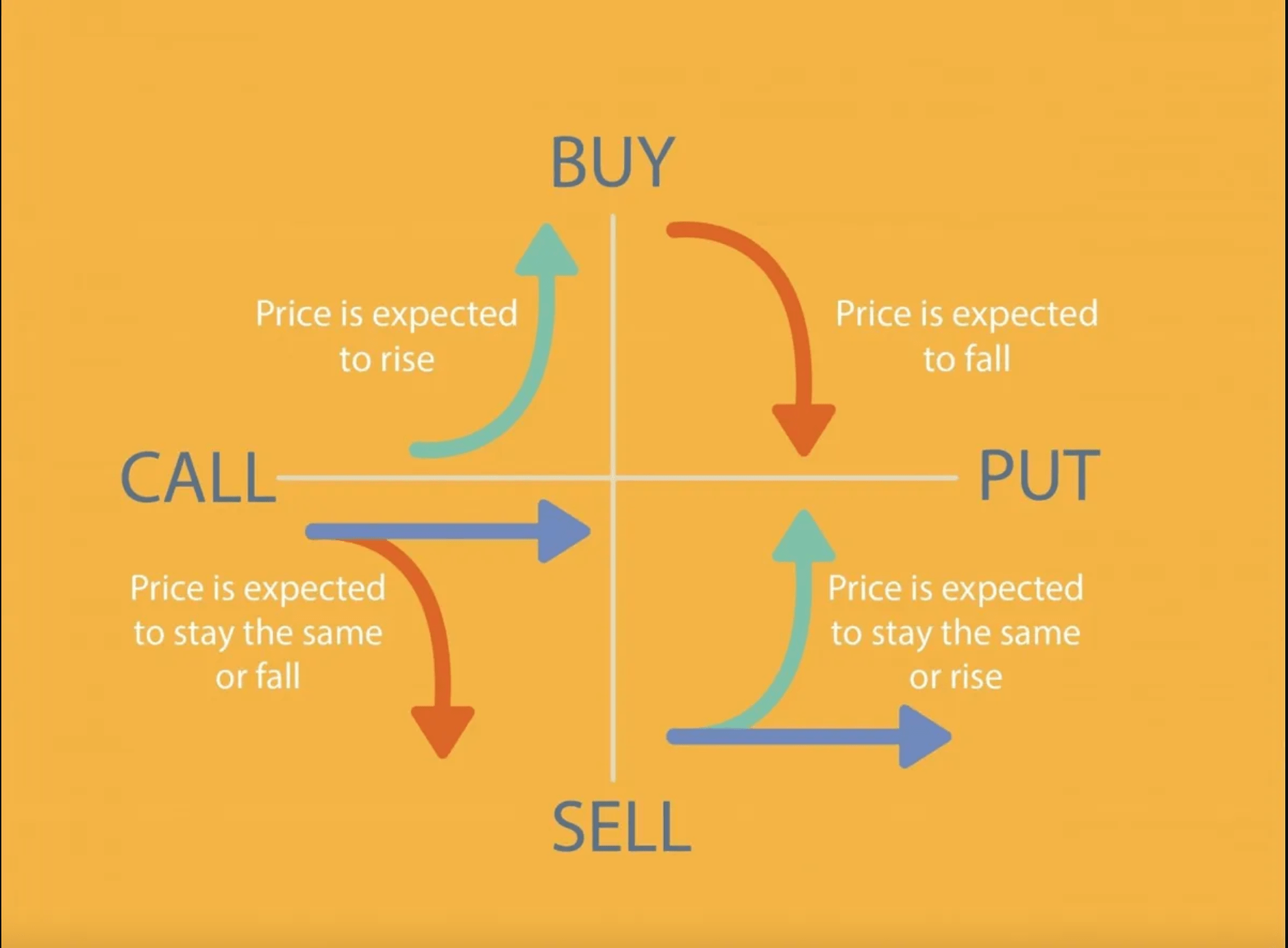
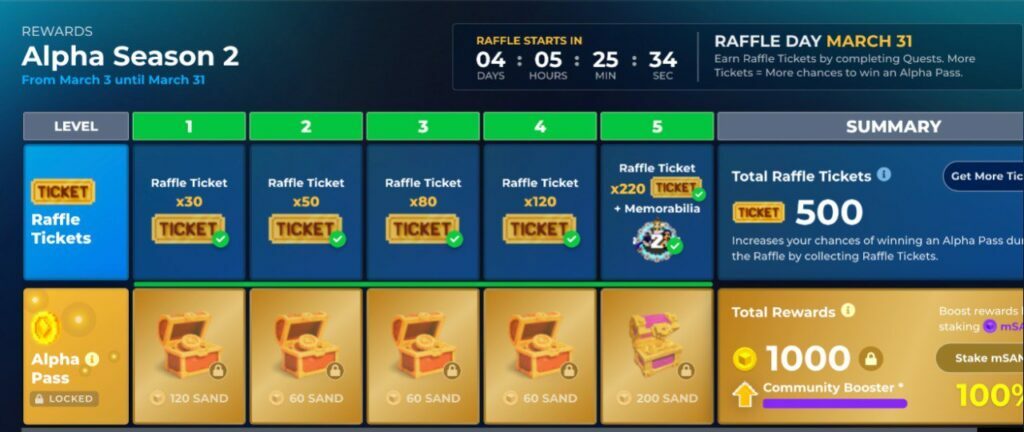
What do you think about the future of gaming? In may opinion gaming industry become bigger and bigger as time pass by, the first game created was a black and white graphics with a little time frame movement and as of now there is a game in cellphone, pc, xbox and so on that our gaming industry is evolving and i think in the future there is a possibility that they created a game that you will you will goes directly into the game even in reality you are just laying in bed, then the movements that you are doing in the game is made by your brain that the game can detect which is be a futuristic type of game but soon i still dreaming that someone will do it and be the game put more thrill and adventurous! 🎉🎉